Thank you for downloading!
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive email updates about our work, get connected and support Australians impacted by eczema. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Subscribe NowEczema is a chronic skin condition but, as the saying goes, one size does not fit all. While common symptoms include dry, scaly skin, redness and itchiness that may be intense, there are in fact seven different types of eczema, all of which have their own unique characteristics and triggers.
Eczema types
Fact: The most common form of eczema, it usually starts in childhood and can be long-lasting.
Symptoms: A rash often forms in the creases of the elbows or knees; skin in rash areas may turn lighter or darker or get thicker; small bumps may appear and leak fluid if scratched; babies often get the rash on their scalp and cheeks; the skin can get infected if scratched.
Causes: Genetic factors, dry skin, immune system problems, environmental triggers.
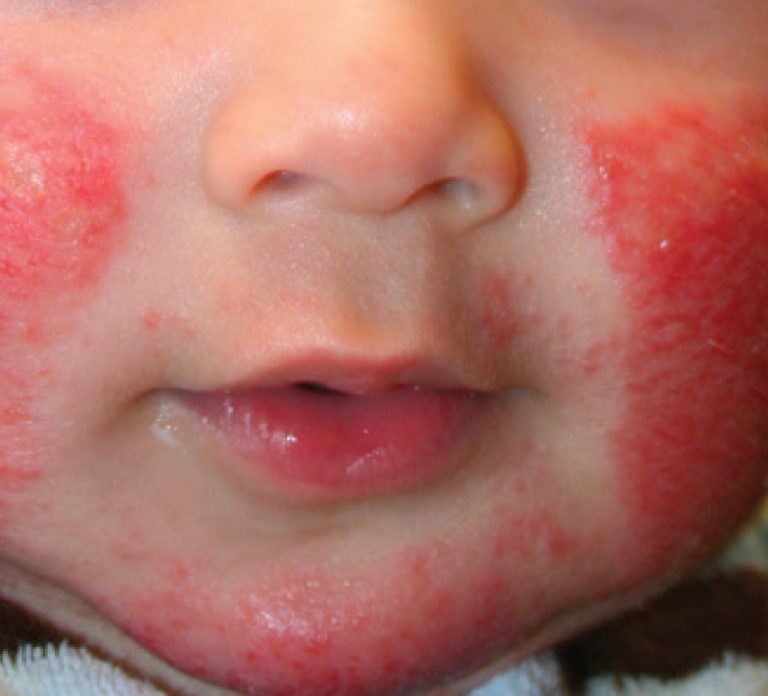
Atopic Dermatitis Atopic Eczema
Eczema types
Fact: The skin becomes inflamed after coming into contact with a substance that irritates or triggers an allergic reaction.
Symptoms: The skin itches, burns and stings; hives (itchy bumps) may pop up; fluid-filled blisters may ooze and crust over; the skin may thicken over time and feel scaly or leathery.
Causes: Common irritants or allergens include detergents, bleach, jewellery, latex, nickel, paint, poisonous plants, skin care products, soaps and perfumes, solvents, tobacco smoke.
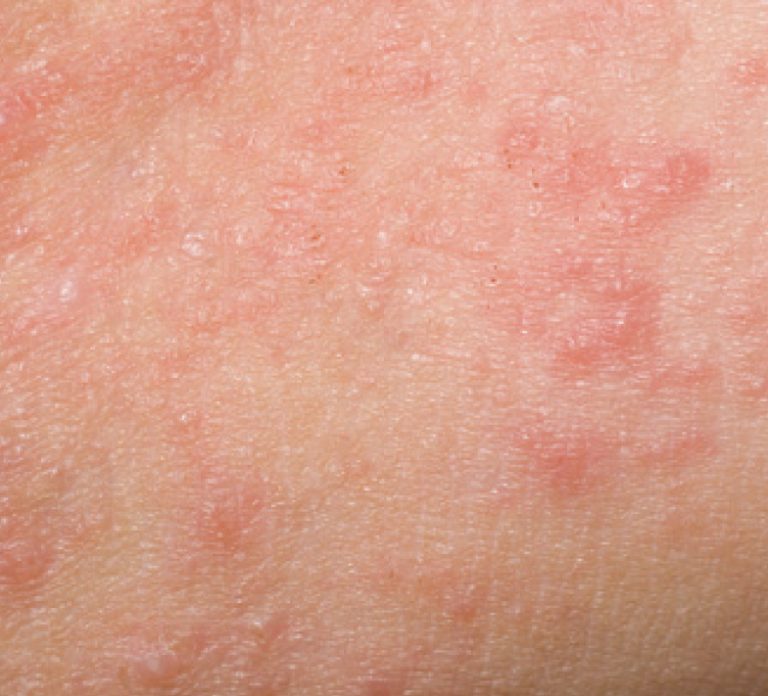
Contact Dermatitis
Eczema types
Fact: More common in women than men (along with younger adults), it causes small blisters to form on the hands and feet.
Symptoms: Fluid-filled blisters form that may itch or hurt; the skin can scale, crack and flake.
Causes: Allergies, damp hands and feet, stress, exposure to substances such as nickel, cobalt or chromium salt.
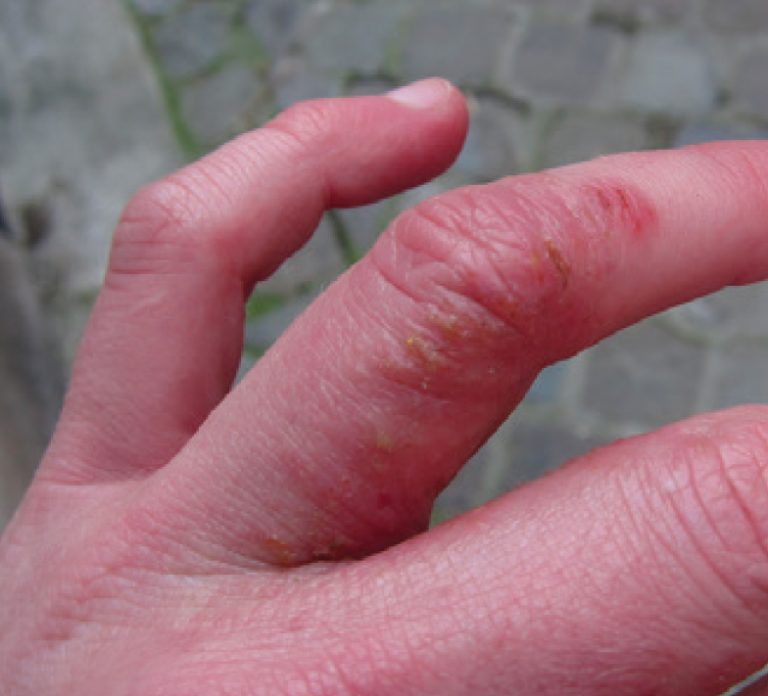
Dyshidrotic Eczema
Eczema types
Fact: Similar to atopic dermatitis but usually confined to one or two patches of skin and rarely goes away without treatment.
Symptoms: Thick, scaly patches form on the arms, legs, back of neck, scalp, bottom of feet, backs of hands or genitals; can be particularly itchy when relaxed or asleep; scratching patches can lead to bleeding and infection.
Causes: Doctors are not certain exactly what causes Neurodermatitis but stress can be a trigger. Commonly seen in people who have other types of eczema.
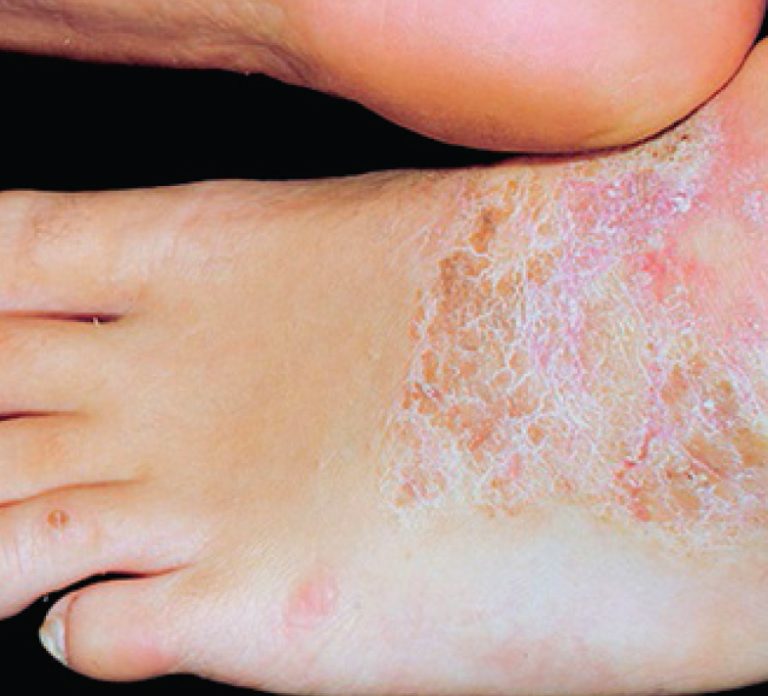
Neurodermatitis
Eczema types
Fact: Round, coin-shaped spots form on the skin. More common in males than females and more likely to affect people who have another type of eczema.
Symptoms: Coin-shaped lesions on arms, legs, torso and/or hands; itching and burning; lesions may ooze liquid or crust over; red, pinkish or brown scaly and inflamed skin around the lesions.
Causes: Dry skin, reaction to an insect bites, allergic reaction to metal or chemicals.
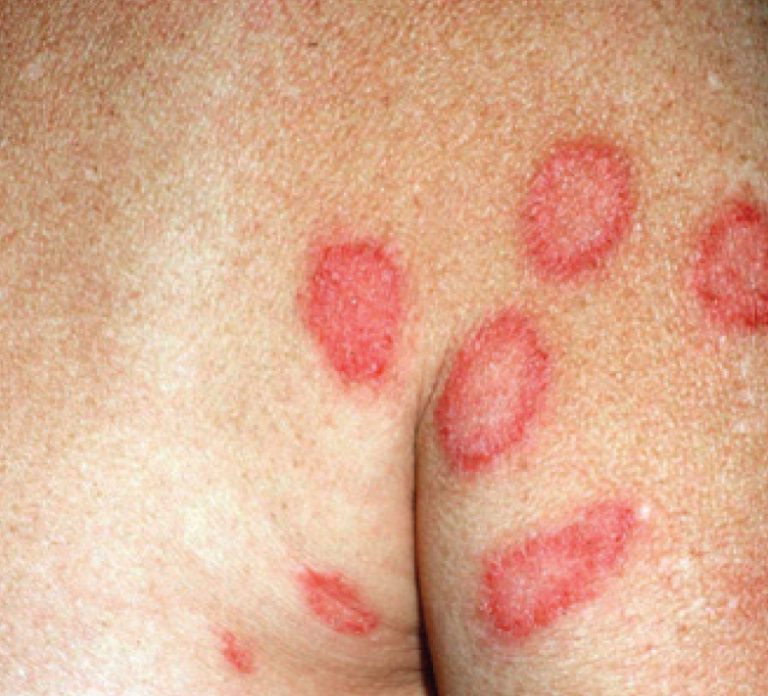
Discoid Eczema
Eczema types
Fact: Associated with poor circulation in the lower legs, with fluid leaking out of weakened veins into the skin to cause swelling, redness, itching and pain. Most common in people older than 50.
Symptoms: Lower part of legs may swell; legs may ache or feel heavy; sufferers likely to also have varicose veins and skin that is dry and itchy; open sores may develop on lower legs and tops of feet.
Causes: Varicose veins, high blood pressure, obesity, vein surgeries, multiple pregnancies, history of blood clots in legs, congestive heart failure, kidney failure, little physical activity, jobs that require excessive sitting or standing.
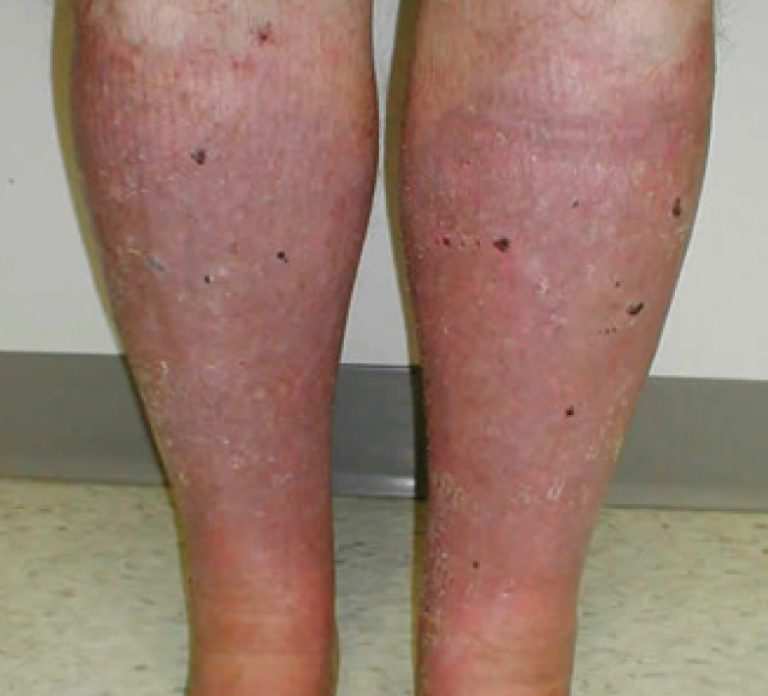
Stasis Dermatitis
Eczema types
Fact: Appears where there are a lot of oil-producing glands like the upper back, nose and scalp. Most common in infants or adults aged 30 to 60 and while it normally clears on its own in infants, it usually follows a pattern of flaring and clearing for years in adults.
Symptoms: Infants most often have scaly, greasy patches on their scalps (aka cradle cap) and can also develop it on their bottoms. Teens and adults can develop redness, swelling and greasy scaling in areas including the eyebrows, sides of nose, mid-chest, upper back and armpits.
Causes: Stress, hormonal changes, illness, harsh detergents, solvents, chemicals and soaps, cold, dry weather, some medications including psoralen, interferon and lithium.
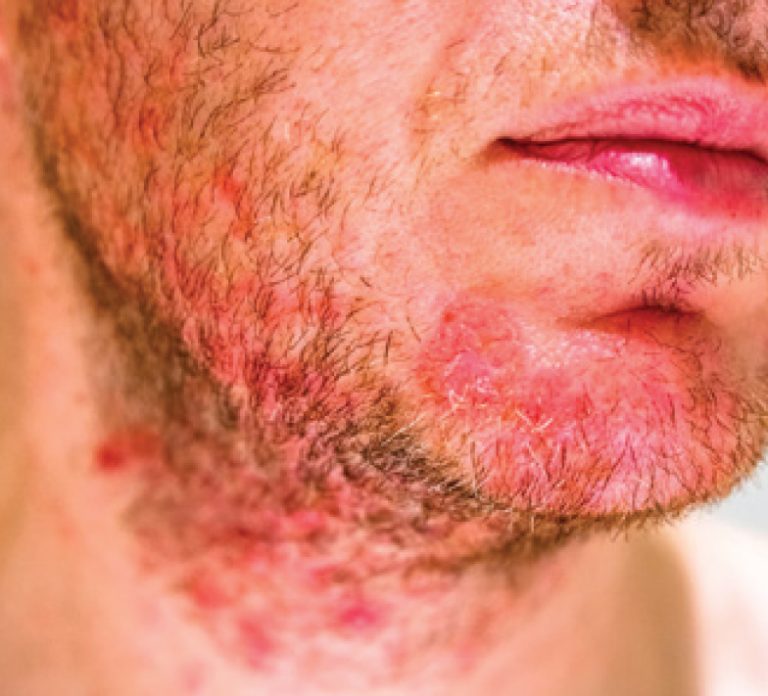
Seborrhoeic Dermatitis
The triggers of eczema are often different for each individual. It can be extremely frustrating as you try to work out the cause of each flare up.
Avoiding triggers and controlling flare ups/inflammation are ways in which you can manage your condition. But there is rarely just one trigger that will be responsible.
e.g. coarse, scratchy wool, synthetic materials like polyester, tags, on clothing
such as soaps and detergents.
Although there may be a link between food allergies and eczema, food is rarely the main eczema trigger (seek doctors/allergist/immunologist advice before eliminating foods)
can both seriously aggravate eczema. Herpes simplex (cold sores) may become widespread and require hospitalisation.
associated with sweating
which cause allergic contact dermatitis such as perfume, preservatives in skincare products, metals such as nickel and many other.
if there is an allergy to household dust mite.
The most common types include atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, nummular eczema, seborrhoeic dermatitis, and stasis dermatitis. Each type has different triggers, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
Visit the Eczema Resource Library to learn more.
Use our Eczema Care Online Toolkit to find out the best way to care for your eczema or your child's eczema.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive email updates about our work, get connected and support Australians impacted by eczema. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Subscribe Now